Home > Servers, Workstation & Backup
Home / Servers, Workstation & Backup
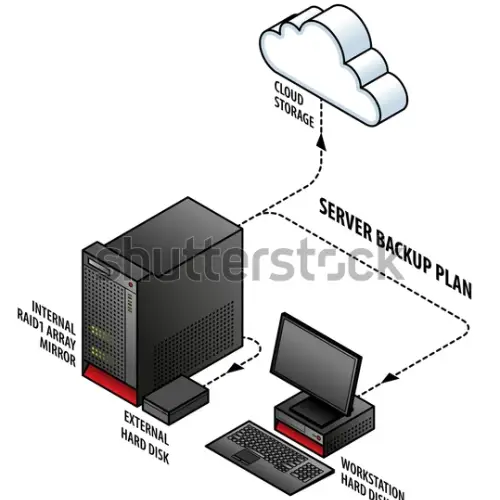
Servers, workstations, and backup systems are essential components of an organization’s IT infrastructure. They serve different purposes and play distinct roles in ensuring the smooth operation, productivity, and data integrity of a business. Here’s an overview of each component:
1. Servers:
- Purpose: Servers are specialized computers designed to provide services, resources, and data to client devices within a network. They handle tasks like data storage, application hosting, email, website hosting, and more.
- Types:
- File Servers: Store and manage files and data, allowing users to access and share resources.
- Web Servers: Host websites and web applications, serving web content to users.
- Database Servers: Manage and store databases, enabling data retrieval and management.
- Email Servers: Handle email communication, storage, and retrieval.
- Application Servers: Run and manage specific software applications that serve multiple clients.
- Print Servers: Manage and control printing tasks within a network.
- Characteristics:
- Servers are typically more powerful and have more resources (CPU, RAM, storage) than workstations.
- They are often housed in data centers or server rooms for centralized management and security.
- Servers are designed for continuous operation and often have redundancy and failover capabilities to minimize downtime.
- They are managed and maintained by IT administrators.
2. Workstations:
- Purpose: Workstations are personal computers used by employees or users to perform tasks such as document processing, software development, graphic design, and more.
- Characteristics:
- Workstations are optimized for individual productivity and often have high-performance hardware.
- They run standard operating systems like Windows, macOS, or Linux.
- Unlike servers, workstations are used for general-purpose tasks and can be highly customized to suit specific user needs.
- They are not typically intended for 24/7 operation and are powered down when not in use.
3. Backup Systems:
- Purpose: Backup systems are essential for data protection and disaster recovery. They ensure that critical data is regularly backed up and can be restored in the event of data loss or system failures.
- Components:
- Backup Software: Manages the backup process, scheduling, and data recovery.
- Backup Storage: Includes external hard drives, network-attached storage (NAS), tape drives, or cloud storage where backup copies are stored.
- Backup Policies: Define what data is backed up, how often backups occur, and how long backup copies are retained.
- Disaster Recovery Plan: Outlines procedures for restoring data and systems in case of a disaster.
- Types:
- Full Backup: Copies all selected data in one go.
- Incremental Backup: Backs up only the changes made since the last backup, reducing storage space and time.
- Differential Backup: Backs up all changes made since the last full backup.
- Importance: Regular backups protect against data loss due to hardware failures, data corruption, accidental deletion, and cyberattacks.
In summary, servers provide services and resources to a network of users, workstations are used by individuals for daily tasks, and backup systems ensure data integrity and recovery in case of emergencies. An organization’s IT infrastructure often includes a combination of these components to meet its specific needs for data management, productivity, and resilience.
