Home > Intrusion Detection
Home / Intrusion Detection
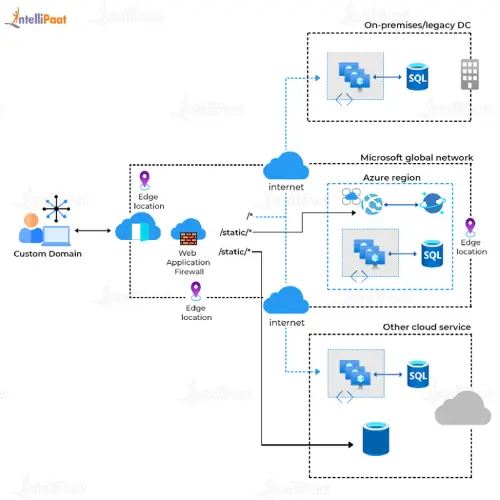
Intrusion detection is a critical component of cybersecurity and physical security systems. It refers to the process of monitoring and identifying unauthorized or suspicious activities or attempts to breach a computer network, system, or physical location. Intrusion detection systems (IDS) are designed to detect and respond to potential threats and security breaches. There are two main types of intrusion detection:
Network Intrusion Detection (NIDS):
- Definition: NIDS monitors network traffic, looking for patterns and signatures that indicate unauthorized or malicious activity.
- How It Works: NIDS systems analyze network packets, looking for anomalies or known attack patterns. They can be signature-based (matching against a database of known attack patterns) or anomaly-based (detecting deviations from established network baselines).
- Deployment: NIDS sensors are typically placed at strategic points within a network, such as at network gateways or critical network segments.
Host Intrusion Detection (HIDS):
- Definition: HIDS focuses on monitoring the activities and files on individual computer systems or hosts.
- How It Works: HIDS systems run on individual host devices and analyze system logs, system files, and user activities for signs of unauthorized access or malicious behavior.
- Deployment: HIDS is deployed on individual hosts, such as servers or workstations, making it effective for protecting specific systems.
Key Concepts and Features of Intrusion Detection:
- Alerts: When an IDS detects a potential intrusion or security breach, it generates alerts or notifications for security personnel to investigate.
- Logs and Reporting: IDS systems maintain logs of detected events, providing a historical record of security incidents.
- False Positives and False Negatives: IDS systems can generate false positives (mistakenly flagging legitimate activity as an intrusion) or false negatives (failing to detect actual intrusions).
- Response: Intrusion detection systems can be configured to trigger automated responses, such as blocking traffic or sending alerts, or they can be used for passive monitoring, with human analysts making decisions based on alerts.
- Integration: IDS can be integrated with other security systems, such as firewalls and security information and event management (SIEM) systems, for a more comprehensive security posture.
- Machine Learning and AI: Some modern IDS solutions use machine learning and artificial intelligence to improve detection capabilities and reduce false positives.
Intrusion detection is a vital part of a layered security strategy, helping organizations identify and respond to security incidents in real-time or after the fact. It plays a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive data, preventing unauthorized access, and maintaining the integrity of computer networks and systems.
