Home > Network Switches, Routers
Home / Network Switches, Routers
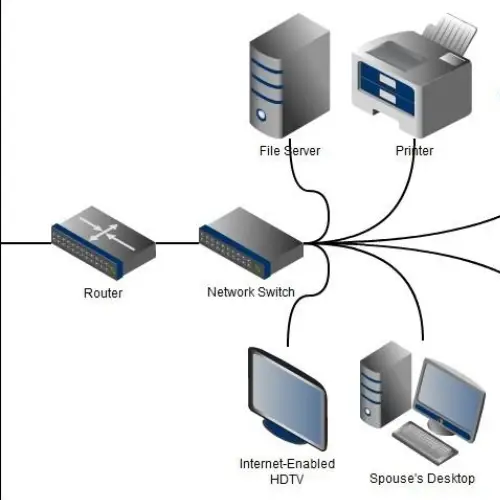
Network switches and routers are fundamental networking devices that play essential roles in data transmission, network management, and connectivity within computer networks. While they both work to facilitate data transfer within a network, they serve distinct purposes and have different functionalities. Here’s an overview of network switches and routers:
Network Switches:
- Purpose: Network switches are used to create a local area network (LAN) by connecting multiple devices within a network, such as computers, printers, servers, and other networked devices. They operate at the data link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model.
- Functionality:
- Packet Forwarding: Switches forward data packets between devices within the same local network based on their MAC (Media Access Control) addresses.
- Broadcast and Collision Domains: Switches create separate collision domains (segments) for connected devices, reducing the likelihood of network collisions.
- Efficiency: Switches improve network efficiency by delivering data directly to the intended recipient, rather than broadcasting it to all devices on the network.
- Use Cases:
- Switches are commonly used in office networks, data centers, and home networks to connect devices within a LAN.
- Managed switches offer additional features such as VLAN support, quality of service (QoS), and network monitoring.
Routers:
- Purpose: Routers connect multiple networks together, allowing data to be transmitted between different networks, such as a local network and the internet. They operate at the network layer (Layer 3) of the OSI model.
- Functionality:
- Packet Routing: Routers determine the best path for data packets to travel between networks, based on their destination IP addresses.
- Network Address Translation (NAT): Routers often use NAT to map multiple private IP addresses to a single public IP address for internet access.
- Firewall and Security: Many routers include firewall features to protect the network from unauthorized access and threats.
- Use Cases:
- Routers are essential for connecting a LAN to the internet, as they manage the traffic between the local network and external networks.
- They are used in homes, businesses, and internet service provider (ISP) networks.
Differences:
- Scope: Switches operate within a single LAN and focus on local data transmission. Routers operate between different networks and handle the routing of data between them.
- Function: Switches primarily forward data at the MAC address level, while routers make routing decisions based on IP addresses.
- Addressing: Switches use MAC addresses to forward data within a LAN, while routers use IP addresses to route data between networks.
- Traffic Handling: Routers can handle traffic between different network protocols and are often equipped with security features, while switches focus on efficient data forwarding within a LAN.
In summary, switches are used for local network connectivity and data forwarding within a LAN, while routers are responsible for connecting multiple networks together and directing data traffic between them. Together, they form the backbone of modern computer networks, allowing devices to communicate both locally and across the internet.
